Anatomy Of The Endoscopic Nasal & Sinus Surgery
The human nose, with its intricate network of passages and sinuses, serves as far more than a mere olfactory organ. Its anatomy plays a vital role in respiration, immune defense, and even voice modulation. Understanding the structure and function of the nasal cavity and sinuses provides valuable insights into various medical conditions and surgical interventions.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Nasal Cavity: Gateway to the Respiratory System
The nasal cavity, positioned centrally in the face, serves as the primary entry point for air into the respiratory system. Its structure is divided into two main chambers by the nasal septum, a thin bony and cartilaginous structure. This septum separates the left and right nasal passages. Each nasal passage is lined with mucous membranes containing millions of tiny hair-like structures called cilia, which help filter impurities and humidify incoming air.
The lateral walls of the nasal cavity are adorned with three bony projections known as turbinates or nasal conchae: the inferior, middle, and superior turbinates. These structures increase the surface area within the nasal cavity, aiding in the warming and humidification of inspired air. They also contribute to directing airflow and promoting the sense of smell.
Functions of the Nasal Cavity: Beyond Smelling
While the sense of smell, or olfaction, is a prominent function of the nasal cavity, its role extends far beyond mere odor detection. The nasal mucosa plays a crucial role in air conditioning, where incoming air is warmed, humidified, and filtered. This process is essential for maintaining optimal conditions for the respiratory system.
Additionally, the nasal cavity serves as a frontline defense against pathogens. Mucus secretions trap foreign particles, including bacteria and viruses, while the immune cells present in the nasal mucosa help neutralize these threats. This defense mechanism is crucial in preventing respiratory infections.
Moreover, the nasal cavity contributes to voice resonance and modulation. Changes in the shape and size of the nasal passages can affect the quality of one’s voice, highlighting the interconnectedness of nasal anatomy and vocal function.
The Intricacies of Nasal Sinuses
Adjacent to the nasal cavity lie four pairs of air-filled cavities known as the paranasal sinuses: the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary sinuses. These sinuses are lined with mucous membranes similar to those found in the nasal cavity and are connected to it via small openings called ostia.
The frontal sinuses, situated behind the forehead, aid in reducing the weight of the skull and contribute to voice resonance. The ethmoid sinuses, located between the eyes, are a complex system of interconnected air cells. They play a role in humidification, and voice resonance, and are critical for the sense of smell. The sphenoid sinuses, positioned behind the ethmoid sinuses, have a significant role in voice modulation and are near important neurovascular structures. Finally, the maxillary sinuses, the largest of the paranasal sinuses, are located beneath the cheeks and serve to lighten the skull, provide insulation for dental roots, and contribute to voice resonance.
Clinical Significance and Pathology
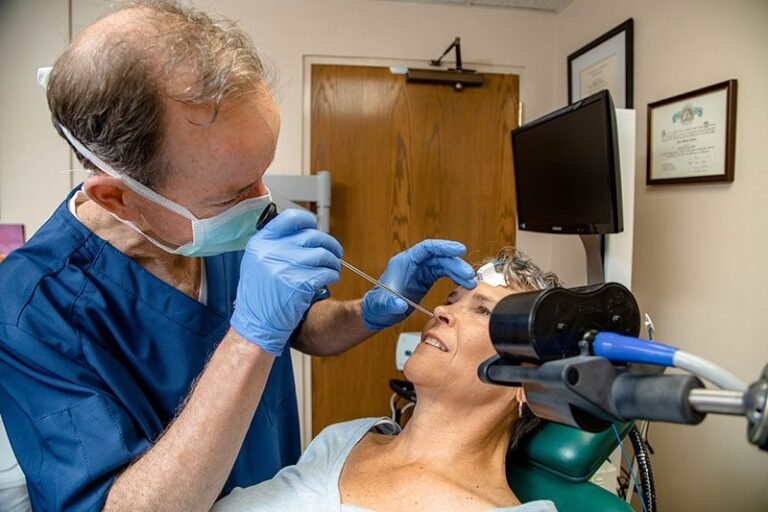
Disruptions in the anatomy or function of the nasal cavity and sinuses can lead to various medical conditions, including sinusitis, nasal polyps, deviated septum, and nasal tumors. Endoscopic examination and surgical interventions have become invaluable tools in diagnosing and treating these conditions.
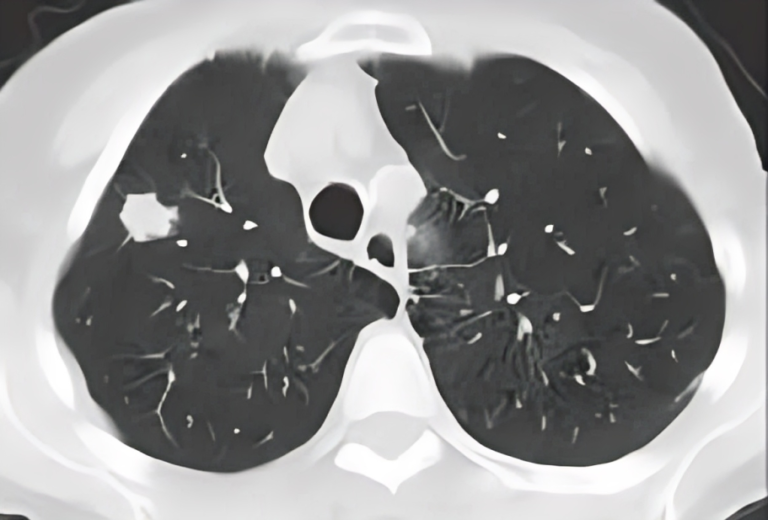
Understanding the intricate anatomy of the nasal cavity and sinuses is essential for healthcare professionals involved in the management of respiratory disorders, otolaryngology (ENT), and rhinology. Advances in imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), have further enhanced our ability to visualize and comprehend these structures in both health and disease.
conclusion
the nasal cavity and sinuses represent a fascinating and multifaceted anatomical system with diverse functions beyond mere olfaction. Their intricate structure and physiological roles underscore their importance in respiratory health, immune defense, and even vocalization. A comprehensive understanding of nasal anatomy forms the foundation for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management of a wide range of medical conditions.
Also, Follow us on Instagram