Exploring Tympanometry and Audiometry: Key Tools in Assessing Hearing Health.
Hearing plays a vital role in our daily lives, influencing communication, social interactions, and overall well-being. Tympanometry and audiometry are two essential diagnostic tools employed by audiologists to assess various aspects of hearing health. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of tympanometry and audiometry, exploring their functions, procedures, and the valuable information they provide in understanding and addressing hearing-related issues.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
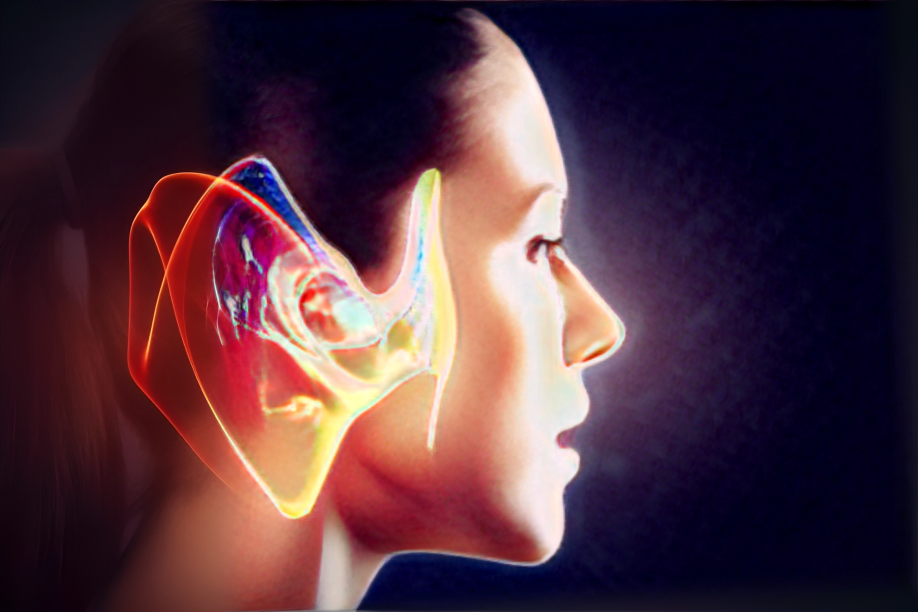
Tympanometry: Unraveling Middle Ear Function
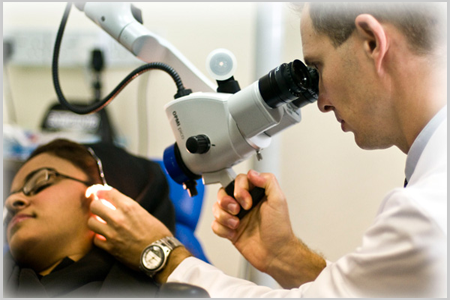
Tympanometry is a diagnostic test designed to evaluate the function of the middle ear, focusing on the mobility of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the conduction bones. This test is particularly useful in identifying conditions such as otitis media (middle ear infection), eustachian tube dysfunction, and other middle ear abnormalities.
Procedure:
- Sealing the Ear Canal: A small probe is gently inserted into the ear canal, creating an airtight seal. This probe may also include a tiny speaker that emits varying air pressure levels.
- Pressure Changes: The air pressure within the ear canal is systematically altered, causing the eardrum to move back and forth. The probe measures the compliance of the eardrum at different pressure levels.
- Graphical Representation: The results are graphically represented on a tympanogram, depicting the compliance of the eardrum and indicating the status of the middle ear.
Key Insights from Tympanometry:
- Peak Compliance: The peak of the tympanogram indicates the point of maximum eardrum movement, providing insights into middle ear function.
- Ear Canal Volume: Tympanometry also measures the volume of the ear canal, helping to identify any abnormalities in the ear’s physical structure.
Audiometry: Mapping the Auditory Landscape
Audiometry is a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s hearing ability, examining the entire auditory system from the outer ear to the brain’s interpretation of sound. This test is crucial in identifying hearing loss, its degree, and potential contributing factors.
Procedure:
- Pure-Tone Audiometry: The patient is exposed to a series of pure-tone sounds at various frequencies and intensities. The individual responds by indicating when they hear the sound, and the audiologist charts the results on an audiogram.
- Speech Audiometry: This assesses the ability to hear and understand spoken words at different volume levels. It helps determine the patient’s speech reception threshold and speech discrimination ability.
- Bone Conduction Testing: Involves the use of a vibrating device placed behind the ear to assess inner ear function, bypassing the outer and middle ear.
Key Insights from Audiometry:
- Degree of Hearing Loss: The audiogram provides a visual representation of the patient’s hearing thresholds at different frequencies, helping determine the degree and type of hearing loss.
- Configuration of Hearing Loss: Audiometry reveals whether hearing loss is uniform across frequencies or if certain frequencies are more affected than others, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion:
Tympanometry and audiometry are indispensable tools in the realm of audiology, offering valuable insights into the intricate mechanisms of hearing. From assessing middle ear function to mapping the auditory landscape, these diagnostic tests enable healthcare professionals to diagnose hearing-related issues accurately and tailor interventions to individual needs. Regular hearing assessments using these tools contribute to early detection and proactive management, enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals with hearing challenges.