Tympanometry and Audiometry: Exploring Diagnostic Tools for Hearing Health.
Hearing loss is a prevalent yet often overlooked health concern affecting millions of individuals worldwide. From infants to the elderly, hearing impairment can significantly impact the quality of life, communication abilities, and overall well-being. In the realm of audiology, tympanometry and audiometry emerge as indispensable diagnostic tools, playing a crucial role in assessing and managing various auditory conditions. Let’s delve into the intricacies of these two procedures and understand their significance in preserving hearing health.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
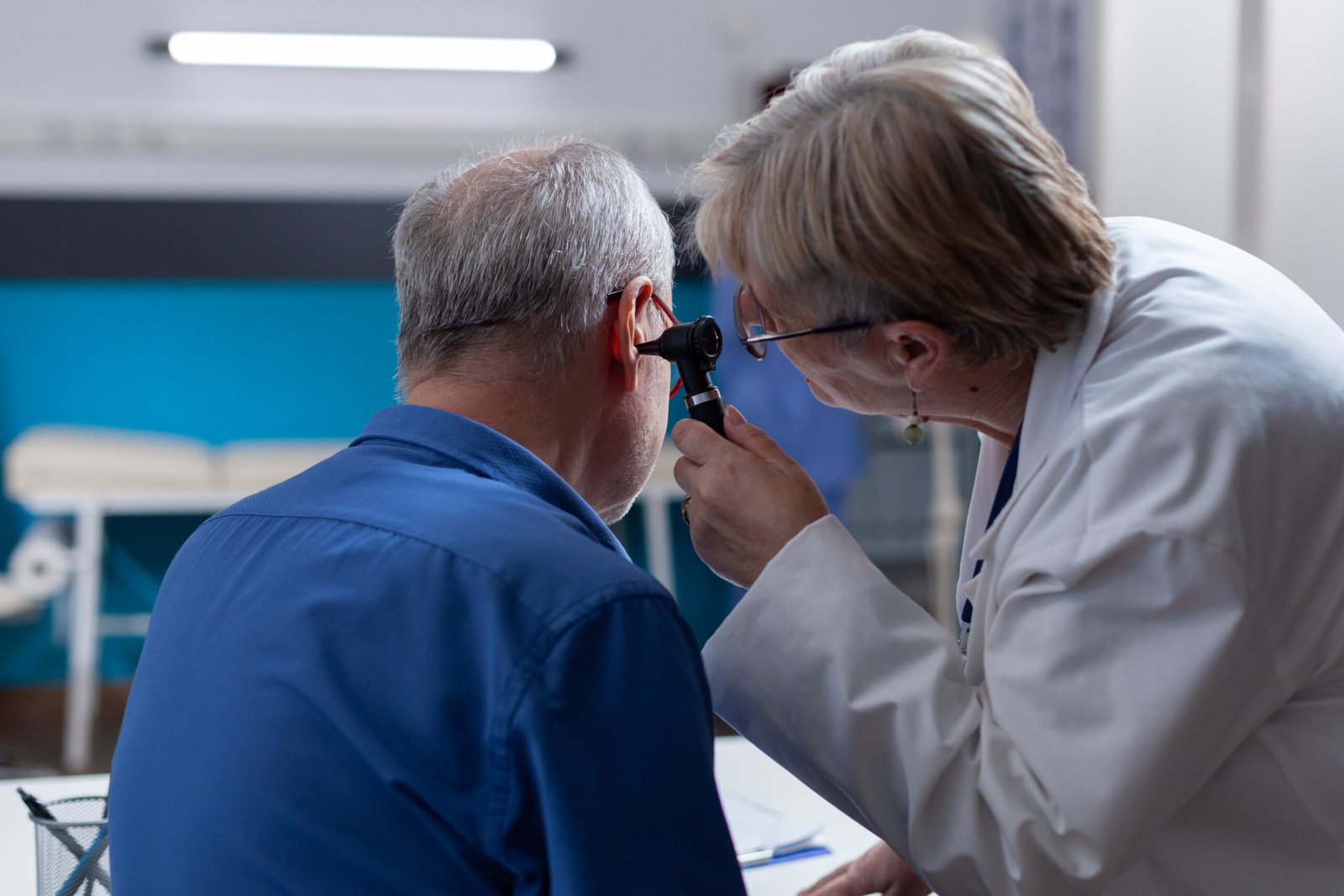
Tympanometry, a cornerstone of diagnostic audiology, evaluates the functionality of the middle ear and the mobility of the eardrum (tympanic membrane). This non-invasive procedure involves the use of a tympanometer, a specialized device that generates sound waves and measures the responses from the middle ear. During tympanometry, a probe is gently inserted into the ear canal, and air pressure variations are introduced to assess the movement of the eardrum and the integrity of the middle ear system.
The results of tympanometry are depicted graphically on a tympanogram, providing valuable insights into the condition of the middle ear. A normal tympanogram typically exhibits a peak indicating optimal eardrum mobility and middle ear pressure. Conversely, abnormalities in the tympanogram may indicate conditions such as fluid accumulation in the middle ear (otitis media with effusion), eustachian tube dysfunction, perforated eardrum, or the presence of middle ear pathology.
By providing objective data on middle ear function, tympanometry assists audiologists and otolaryngologists in diagnosing and monitoring various auditory disorders. It serves as a valuable tool in the assessment of patients with hearing loss, recurrent ear infections, and other middle ear abnormalities.
Complementing tympanometry is audiometry, a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s hearing abilities. Audiometry measures the threshold of hearing across different frequencies, enabling clinicians to assess the extent and nature of hearing loss. This diagnostic procedure is typically conducted in a sound-treated booth using specialized equipment called an audiometer.
During audiometry, patients are presented with sounds of varying frequencies and intensity levels through headphones or insert earphones. They are instructed to respond whenever they hear a sound by pressing a button or raising their hand. The audiologist records the patient’s responses, plotting them on an audiogram—a graph that illustrates the patient’s hearing thresholds at different frequencies.
Audiometry provides critical information about the type, degree, and configuration of hearing loss. It helps clinicians identify sensorineural hearing loss (caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve), conductive hearing loss (resulting from problems in the outer or middle ear), and mixed hearing loss (a combination of sensorineural and conductive components). Additionally, audiometry aids in determining the appropriate course of intervention, whether it be hearing aids, cochlear implants, auditory rehabilitation, or medical/surgical management.
The integration of tympanometry and audiometry in clinical practice enhances the accuracy of diagnosis and facilitates tailored interventions for individuals with hearing impairment. By employing these diagnostic tools, healthcare professionals can address hearing-related concerns promptly, improve communication outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of life for their patients.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
for the conclusion
tympanometry and audiometry represent indispensable pillars of diagnostic audiology, offering valuable insights into the functioning of the middle ear and the auditory system. Through meticulous assessment and interpretation of tympanometric and audiometric data, clinicians can formulate personalized treatment plans that address the unique needs of individuals with hearing loss. As we continue to advance in the field of audiology, these diagnostic tools will undoubtedly remain essential in our efforts to preserve and optimize hearing health for all.
For any further queries, Plz visit https://drshravan.in/or you can check our social media accounts, Facebook, Instagram